the complexity of food and other production systems in different ecologies, locations and cultures so integrating food and nutritional security with natural resource management.
6. Determine who pays for the remediation of overexploi-tation and/or pollution of the natural resource system on which everyone depends.
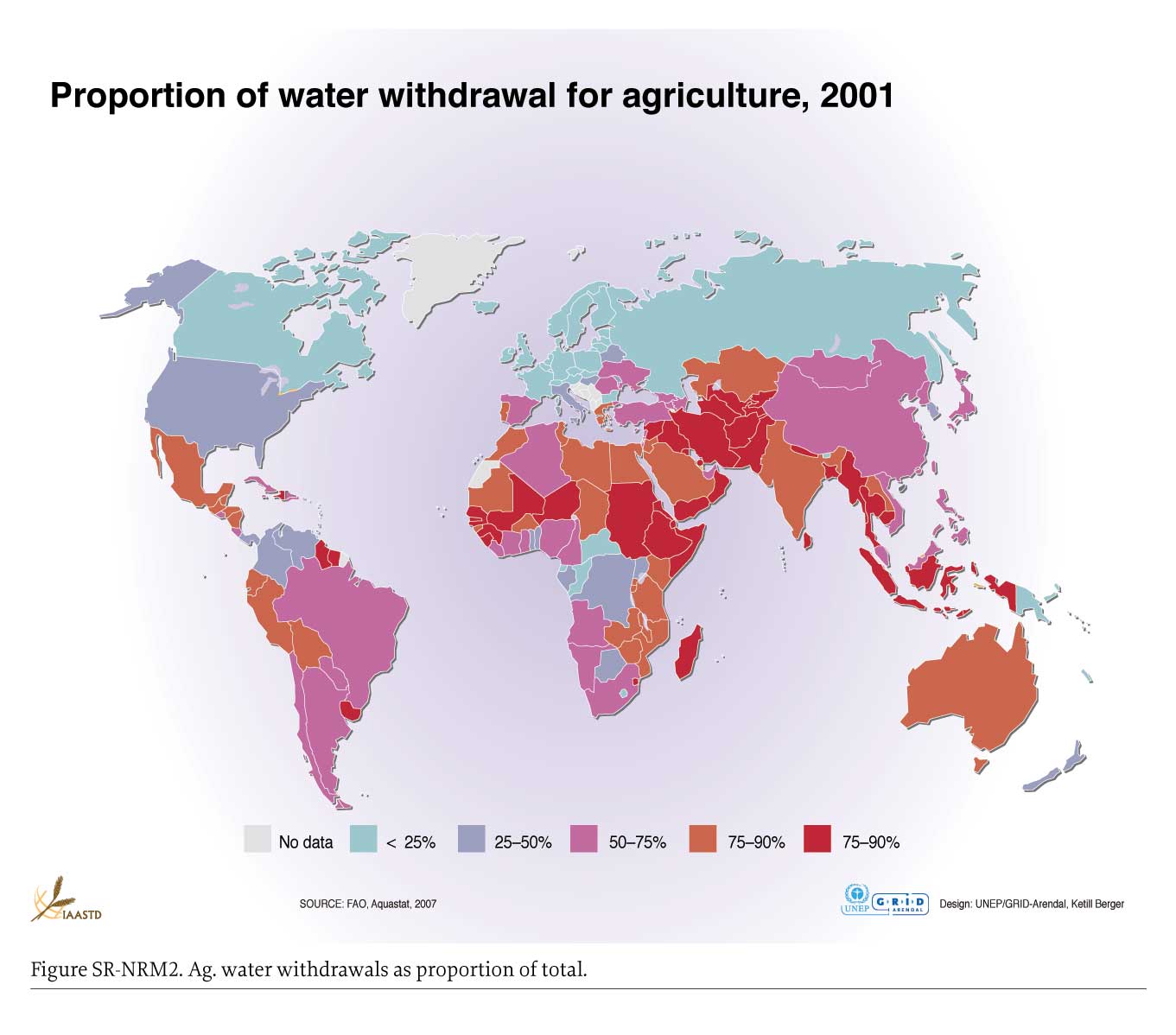
Options for action relative to development and sustainability goals
The AKST available to resolve NRM exploitation issues like the mitigation of soil fertility depletion through synthetic inputs and natural processes, and the impacts of tillage on compaction and organic matter decomposition are often available and well understood. However, there is a need for greater knowledge and understanding of interactions between the agricultural system and the natural environment. Nevertheless, the resolution of natural resource challenges will demand new and creative approaches by stakeholders with diverse backgrounds, skills and priorities. Capabilities for working together at multiple scales and across different social and physical environments are not well developed. For example, farmer groups and civil society members have |
|
rarely been involved in agricultural research, in shaping natural resource management policy, or in working partnerships with the private sector to achieve integrated natural resource management.
Causes of natural resource degradation and of declining productivity are multiple and complex. New AKST based on multidisciplinary approaches (biophysical, behavioral and social) is necessary for a better understanding of this complexity in NRM [NAE SDM Key Message 5; SSA Chapter 5].
Identify and resolve underlying causes of declining productivity embedded in natural resource mismanagement through the adaptation of existing technologies and the creation of innovative solutions.
• Land degradation and nutrient depletion: The degradation of land is most often attributed to factors such as the loss of vegetation due to deforestation, overgrazing, land clearance, land abandonment, and inappropriate agricultural practices. It arises from population pressure, lack of appropriate technical support and knowledge, unavailability of inputs (fertilizers, water), conflicting social pressures, commercial incentives, sub- |